In ITIL 4, Practices are replacing the Services Management Processes known from before. Get the complete overview of all practices here.
Table of Contents
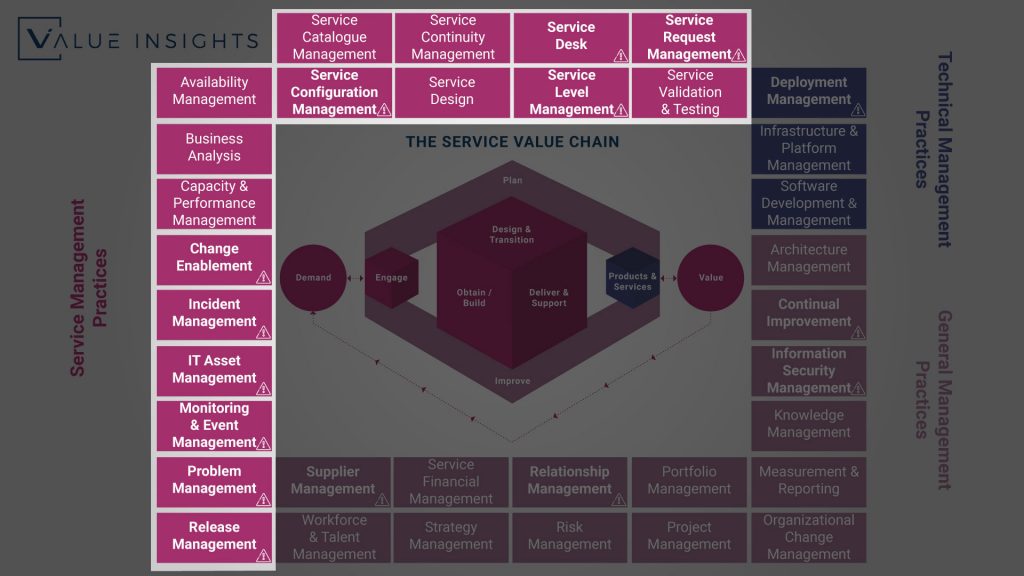
The ITIL 4 Practices Overview
PeopleCert has published the ITIL 4 Practice guides, which are available for download to PeopleCert Plus subscribers. If you want to learn more, please have a look at our article about the ITIL 4 Practices guides.
Since we cannot go into details here, this article is meant to give you a short overview of all ITIL 4 Practices available. For a better understanding, I will also mention the purpose statement for each Practice.
The bold Practices marked with the exclamation mark are the ones, which are part of the ITIL 4 Foundation course. An out of those, there are seven, which are the most important ones. If you want to learn more about this, please have a look at our ITIL 4 Foundation Study Guide.
The Technical Management Practices
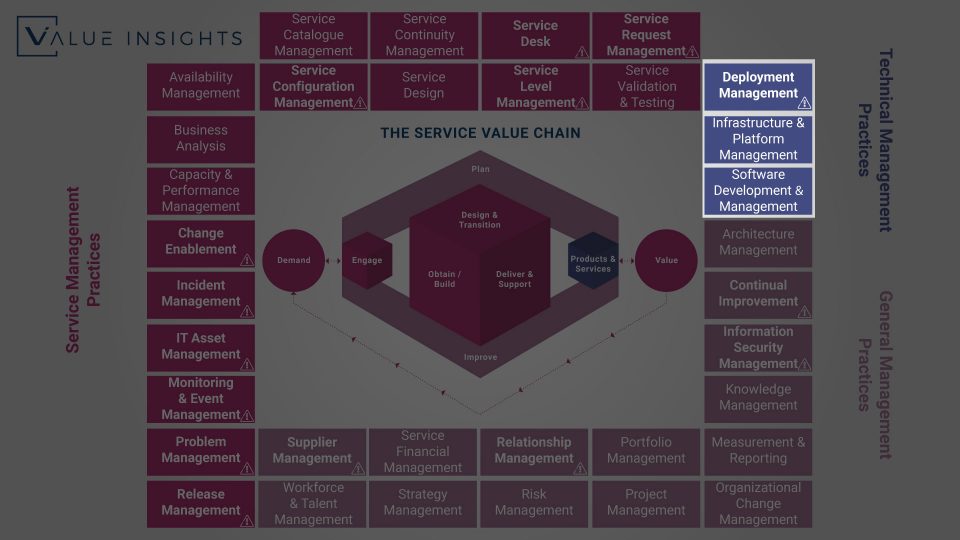
Deployment Management
Purpose
To move new or changed hardware and software components, processes, documentations or any other configuration items to live environments (e.g. PROD). Furthermore, the Deployment Management Practice may be involved in the deployment of components to other environments (e.g. Staging or Testing).
Infrastructure & Platform Management
Purpose
To oversee and manage the platforms and infrastructure elements utilized by the organization. Ideally, this Practices also allows the organization to efficiently monitor the available technical solutions belonging to the organization or even integrated external service providers.
Software Development & Management
Purpose
To ensure that applications meet the needs of stakeholders (internal and external) in terms of Utility and Warranty, meaning functionality, reliability, availability, maintainability, compliance and auditability.
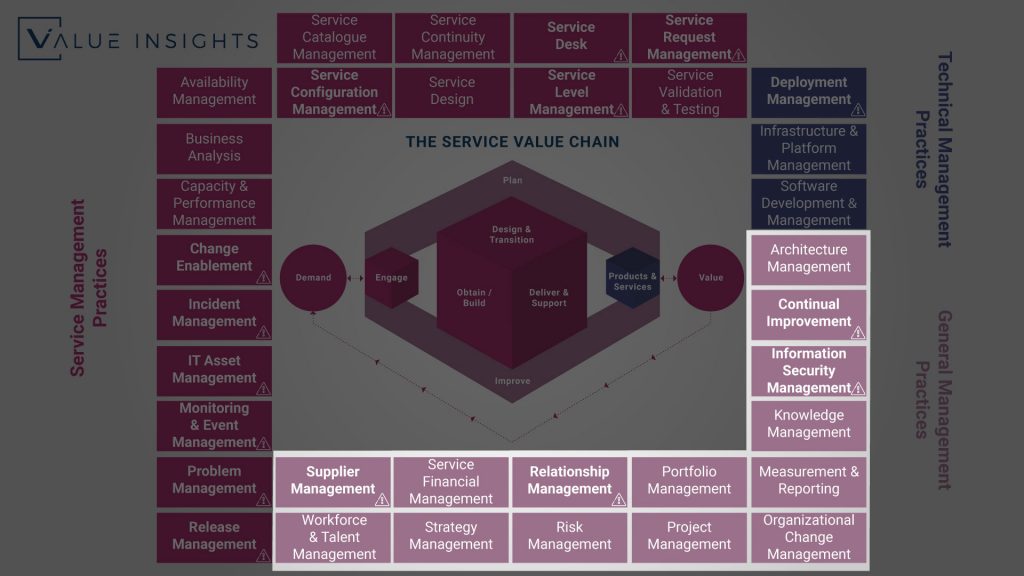
Architecture Management
Purpose
To explain all the different elements that are forming organizations. It explains how these elements interrelate with one another, enabling the organization to effectively and efficiently achieve its current and future objectives. Architecture Management provides the principles, standards and tools that enable organizations to manage complex change in a structured and agile way.
Continual Improvement
Purpose
To align the organizations’ practices and services with ever-changing business needs through the continual improvement of products, services, practices and all other elements that are involved in the management of products and services.
Information Security Management
Purpose
To protect the information needed by the organization to conduct its business. This includes understanding and managing risks to the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information, as well as other aspects of information security such as authentication and non-repudiation.
Knowledge Management
Purpose
To maintain and improve the effective, efficient and convenient use of information and knowledge across the organization.
Measurement & Reporting
Purpose
To support good decision-making and continual improvement by decreasing the levels of uncertainty. This is achieved by collecting relevant data on various managed objects and by assessing this data in an appropriate context. Managed objects may include products, services, practices, Service Value Chain activities, teams, individuals, suppliers, partners and the organization as a whole.
Organizational Change Management
Purpose
To ensure that changes in the organization are implemented smoothly and successfully, and that lasting benefits are achieved by managing the human aspects of changes.
Portfolio Management
Purpose
To ensure that the organization has the right mix of programmes, projects, products and services to execute the organization’s strategy within its funding and resource constraints.
Project Management
Purpose
To ensure that all projects in the organization are successfully delivered by planning, delegating, monitoring and maintaining control of all aspects of projects, and ensuring motivation for the people involved.
Relationship Management
Purpose
To establish and nurture links between the organization and its stakeholders at strategic and tactical levels. It includes the identification, analysis, monitoring and continual improvement of relationships with and between stakeholders.
Risk Management
Purpose
To ensure that the organization understands and effectively handles risks. Managing risks is essential to ensuring the ongoing sustainability of an organization co-creating value with and for its customers. Risk management is an integral part of all organizational activities and therefore central to the organization’s Service Value System (SVS).
Service Financial Management
Purpose
To support the organizations’ strategies and plans for Service Management by ensuring that the organizations’ financial resources and investments are being used effectively and efficiently.
Strategy Management
Purpose
To formulate the goals of the organization and adopt the course of action and allocation of resources necessary for achieving those goals. Strategy Management establishes the organizations’ direction, focuses effort, defines or clarifies the organizations’ priorities and provides consistency or guidance in response to the environment.
Supplier Management
Purpose
To ensure that the organizations’ suppliers and their performances are managed appropriately to support the seamless provision of quality products and services. This includes closer, more collaborative relationships with key suppliers to uncover and realize new value and reduce the risk of failure.
Workforce & Talent Management
Purpose
To ensure that the organization has the right people with the appropriate skills and knowledge in the correct roles to support its business objectives. This practice covers a broad set of activities focused on successfully engaging with the organizations’ employees and people resources, including the planning, recruitment, onboarding, learning and development, performance measurement and succession planning.
Availability Management
Purpose
To ensure that services deliver the agreed levels of availability to meet the needs of customers and users.
Business Analysis
Purpose
To analyse a part or the entirety of a business, define its needs and recommend solutions to address these needs and /or solve a business problem. The solution must facilitate value creation for the stakeholders. It enables an organization to communicate its needs in a meaningful way and express the rationale for change.
Capacity & Performance Management
Purpose
To ensure that services achieve the agreed and expected levels of performance and satisfy current and future demand in a cost-effective way.
Change Enablement
Purpose
To maximize the number of successful service and product changes by ensuring that risks have been properly assessed, authorizing changes to proceed and managing the change schedule.
Incident Management
Purpose
To minimize the negative impact of incidents by restoring normal service operation as quickly as possible.
IT Asset Management
Purpose
To plan and manage the full life-cycle of all IT assets, to help the organization maximizing value, controlling costs, managing risks, supporting decision-making about the purchase, reuse or retirement of IT assets and meeting regulatory and contractual requirements.
Monitoring & Event Management
Purpose
To systematically observe services and service components and record and report selected changes of state identified as events. It identifies and prioritizes infrastructure, service, business process and information security events and establishes the appropriate response to those events.
Problem Management
Purpose
To reduce the likelihood and impact of incidents by identifying actual and potential causes of incidents and managing workarounds and known errors.
Release Management
Purpose
To make new and changed services and features available for use.
Service Catalogue Management
Purpose
To provide a single source of consistent information on all services and service offerings, and to ensure that it is available to the relevant audience.
Service Configuration Management
Purpose
To ensure that accurate and reliable information about the configuration of services and the configuration items that support them is available when and where it is needed. This includes information on how configuration items are configured and the relationships between them.
Service Continuity Management
Purpose
To ensure that the availability and performance of a service are maintained at sufficient levels in case of a disaster. It provides a framework for building organizational resilience with the capability of producing an effective response that safeguards the interests of key stakeholders and the organizations’ reputation, brand and value-creating activities.
Service Design
Purpose
To design products and services that are fit for purpose, and that can be delivered by the organization and its ecosystem. This includes planning and organizing people, partners and suppliers, information, communication, technology and practices for new or changed products and services, and the interaction between the organization and its customers.
Service Desk
Purpose
To capture demand for incident resolution and service requests. It should also be the entry point and single point of contact for the service provider for all users.
Service Level Management
Purpose
To set clear business-based targets for service levels, and to ensure that delivery of services is properly assessed, monitored and managed against these targets.
Service Request Management
Purpose
To support the agreed quality of a service by handling all predefined, user-initiated service requests in an effective and user-friendly manner.
Service Validation & Testing
Purpose
To ensure that new or changed products and services meet defined requirements. The definition of service value is based on input from customers, business objectives and regulatory requirement, and is documented as part of the Design and Transition Service Value Chain activity. These inputs are used to establish measurable quality and performance indicators that support the definition of assurance criteria and testing requirements.
Related Blog Posts
Our Mock Exams
Most Popular Posts
 Are you ready to pass the ITIL 4 Foundation exam?... 196.6k views | 107 comments
Are you ready to pass the ITIL 4 Foundation exam?... 196.6k views | 107 comments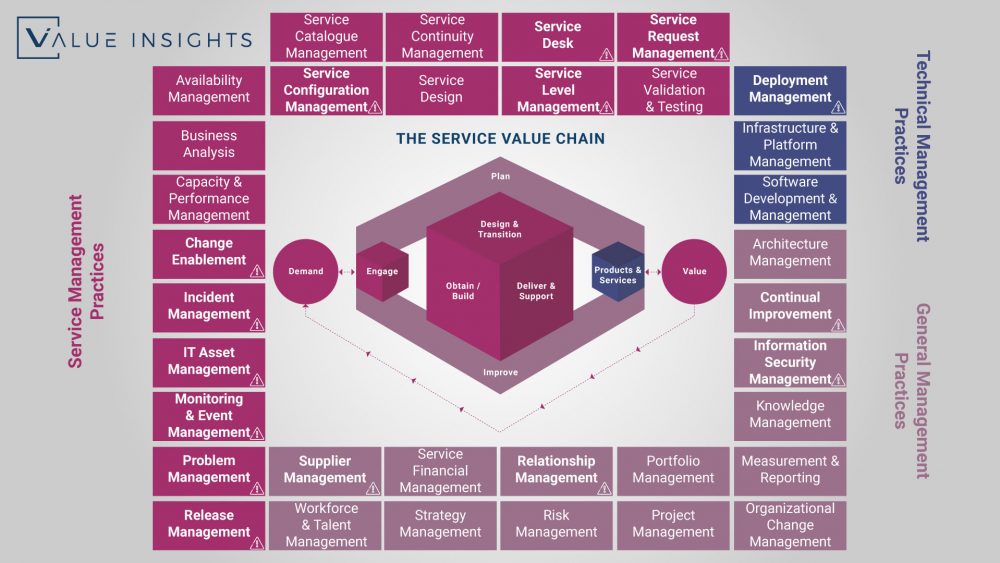 The ITIL 4 Practices Overview 82.8k views | 1 comment
The ITIL 4 Practices Overview 82.8k views | 1 comment Ready for PRINCE2 Foundation? Check this 40 FREE s... 41.8k views | 24 comments
Ready for PRINCE2 Foundation? Check this 40 FREE s... 41.8k views | 24 comments Are you ready to pass the ITIL 4 Foundation exam?... 35.7k views | 0 comments
Are you ready to pass the ITIL 4 Foundation exam?... 35.7k views | 0 comments How to get the ITIL 4 Foundation Digital Badge 34.8k views | 11 comments
How to get the ITIL 4 Foundation Digital Badge 34.8k views | 11 comments




















Hi Ferry
Thanks a lot for your kind feedback and congratulations on passing the exam.
I am glad that our content helped you on your way.
Cheers,
Alex